Protecting Your Speaker (and MCU)
Before you connect your circuit to the 8 Ω speaker, it is critical to ensure that the amplifier output and speaker load will not draw excessive current.
Driving the speaker directly from your MCU will damage both the MCU and the speaker, so always check your circuit before connecting the speaker.
Refer to your speaker datasheet for the exact specifications. A typical 8 Ω speaker datasheet will show:
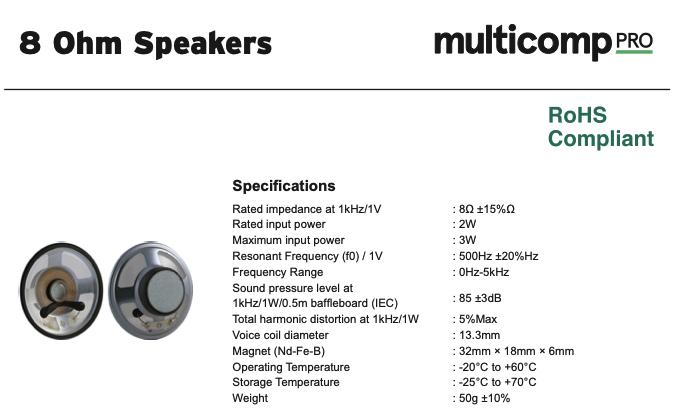
Always verify your output current using a dummy load (resistor) or multimeter before connecting a real speaker!
Step 1: Measure the Output Current
- Build your circuit without the speaker — instead, connect a dummy load such as an 8 Ω resistor to simulate the speaker.
- Use a multimeter to measure the RMS voltage drop across the resistor while your MCU is generating the audio signal.
- From the measured voltage, compute the expected current using Ohm’s law:
\[ I = \frac{V}{R} \]
If you prefer, you can measure current directly by inserting the multimeter in series with the load.
Step 2: Stay Below Safe Limits
An LM386 amplifier can safely drive small speakers, but you must ensure that:
- The output voltage does not exceed approximately 1 V RMS (≈ 2.8 V peak-to-peak) for conservative operation.
- This corresponds to a maximum RMS current of about:
\[ I_{\text{max}} = \frac{1\,\text{V}}{8\,\Omega} = 0.125\,\text{A (125 mA)} \]
Note: According to the speaker datasheet, the rated input power is 2 W (corresponding to ~4 V RMS, ~500 mA) and maximum input power is 3 W. The 1 V RMS limit recommended here (~125 mW) is intentionally conservative to provide a safety margin and prevent distortion. If you need higher volume, you can increase the voltage up to the rated limits, but always verify with measurements first.
To adjust current: - Lower the amplifier gain (to reduce current) - Reduce the input signal amplitude (to reduce current) - Add a small series resistor (to reduce current) - Increase gain/amplitude carefully if you need more volume (stay below 2 W rated power)
Step 3: Never Connect the MCU Pin Directly
Remember:
- MCU GPIO pins can safely source no more than 10–20 mA.
- An 8 Ω speaker draws over 100 mA even at low volume.
If you connect the speaker directly to the MCU, you will fry the MCU output and possibly the speaker.
Always use the LM386 amplifier to buffer the signal and supply sufficient current.
Quick Reference
| Parameter | Recommended Limit (Conservative) | Datasheet Maximum |
|---|---|---|
| Speaker impedance | 8 Ω | 8 Ω ±15% |
| Max safe RMS voltage | ~1 V | ~4 V (2 W rated) |
| Max RMS current | ~125 mA | ~500 mA (2 W rated) |
| Rated input power | — | 2 W |
| Maximum input power | — | 3 W |
| MCU GPIO output current | <20 mA | — |
By following these steps, you’ll protect both your hardware and your hearing while getting clean audio output from your MCU.