Lattice Radiant Installation Instructions
Introduction
Lattice Radiant is the synthesis tool provided by Lattice Semiconductor for targeting their FPGA devices.
Download
Download the software installer from Lattice’s website for your operating system from this link Lattice Radiant Software. (Windows and Linux only. You will need to use virtualization to use Radiant on Mac.). You will also need to create an account to access the download.
Working with the UPduino v3.1 on macOS
I use the Windows version in a Parallels Windows 11 Virtual Machine. The synthesis and simulation works without a hitch but the programming is finicky. I suspect it has something to do with some wonkiness with the USB drivers and the Virtual Machine. To work around this, you can use the openFPGALoader project which is universal utility for programming FPGAs. Instructions for installation and use can be found here.
The easiest way is to directly install it as a Homebrew formula:
brew install openfpgaloaderAfter installation, to program our UPduino v3.1 board, use the command:
openFPGALoader -b ice40_generic -c ft232 -f <path_to_.bin_file>Installing FTDI Drivers
To program the UPduino on Windows, you’ll need to install FTDI drivers if they’re not already installed. To do so, go to the Virtual COM Port (VCP) drivers page and download the appropriate drivers for your system.
For M-series Macs virtualizing Windows, you will need to download the files for an ARM architecture since your installation of Windows is likely using the native ARM architecture instead of virtualizing an x64 instruction set.
Installation
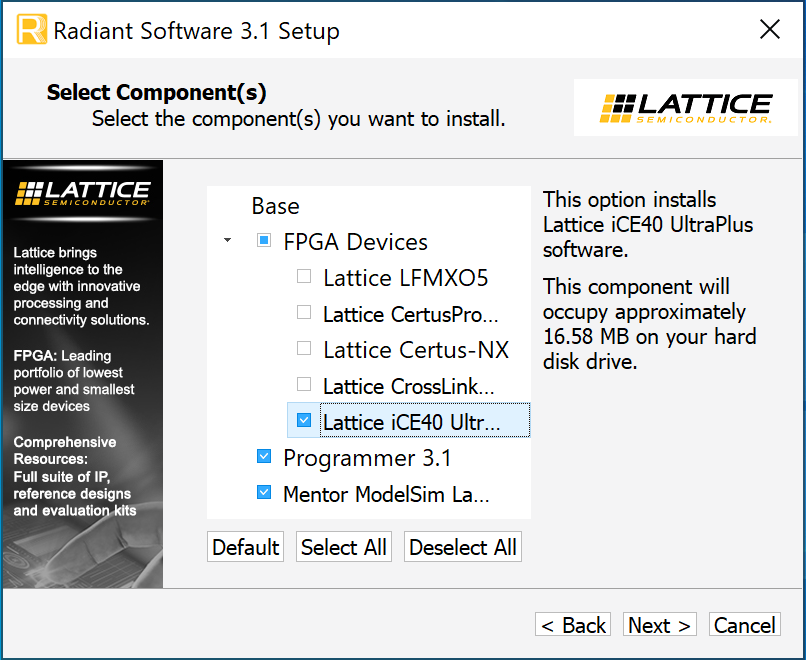
As part of the installation, make sure to select the iCE40 UltraPlus family device support package along with the Programmer and Mentor QuestaSim Lattice Edition. After this menu, click through to finish the installation process.
Licensing
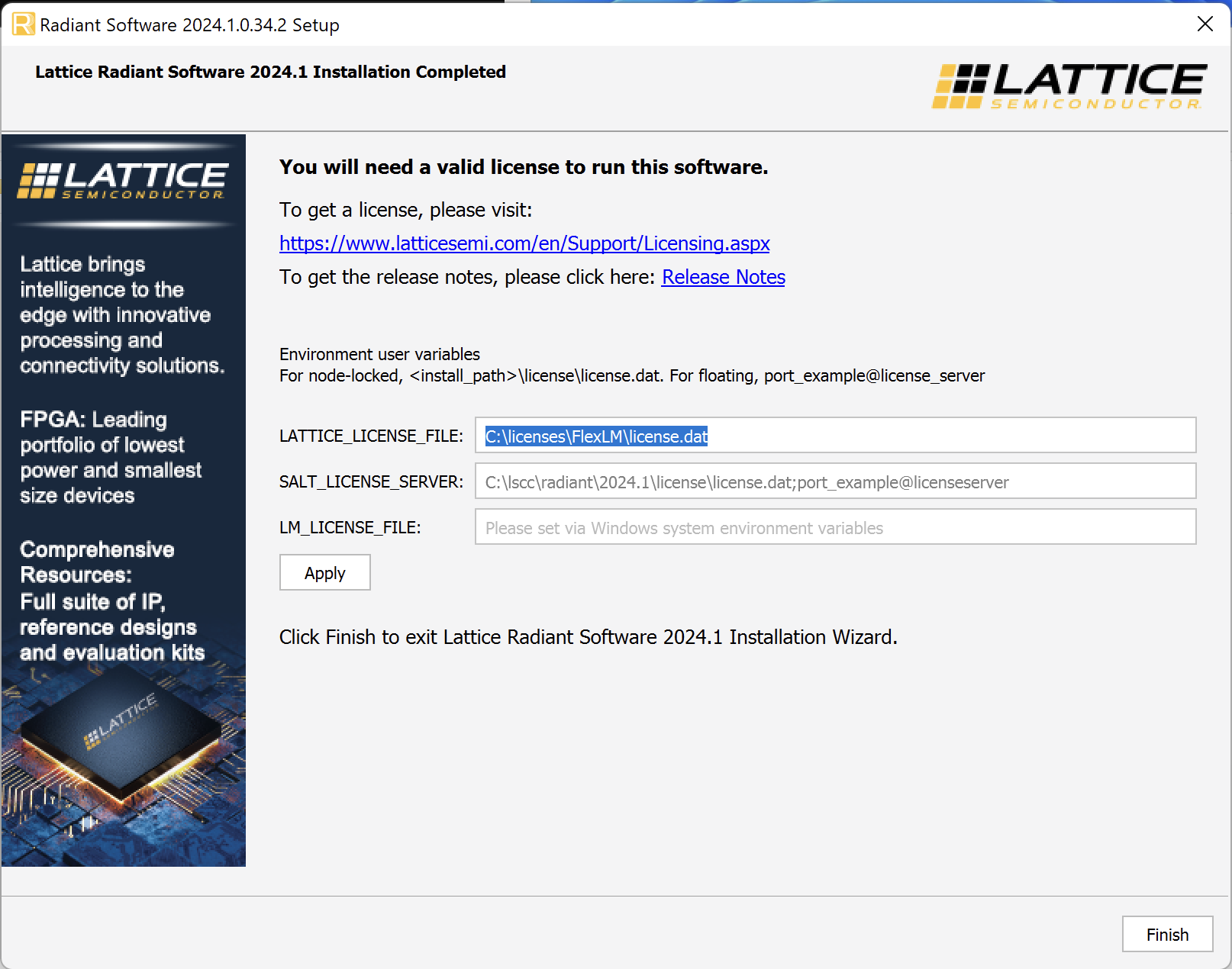
To run Radiant you will need to also request and install a license for the software. Navigate here and request a node-locked license. This license is designed to be run on a single computer.
To download the license you will need to find your Host Network Interface Card (NIC) address. To find the NIC address, follow the steps below.
For Windows, from an MS-DOS window (command prompt), use the ipconfig /all command
For Linux, from the command prompt, use the ifconfig -a command
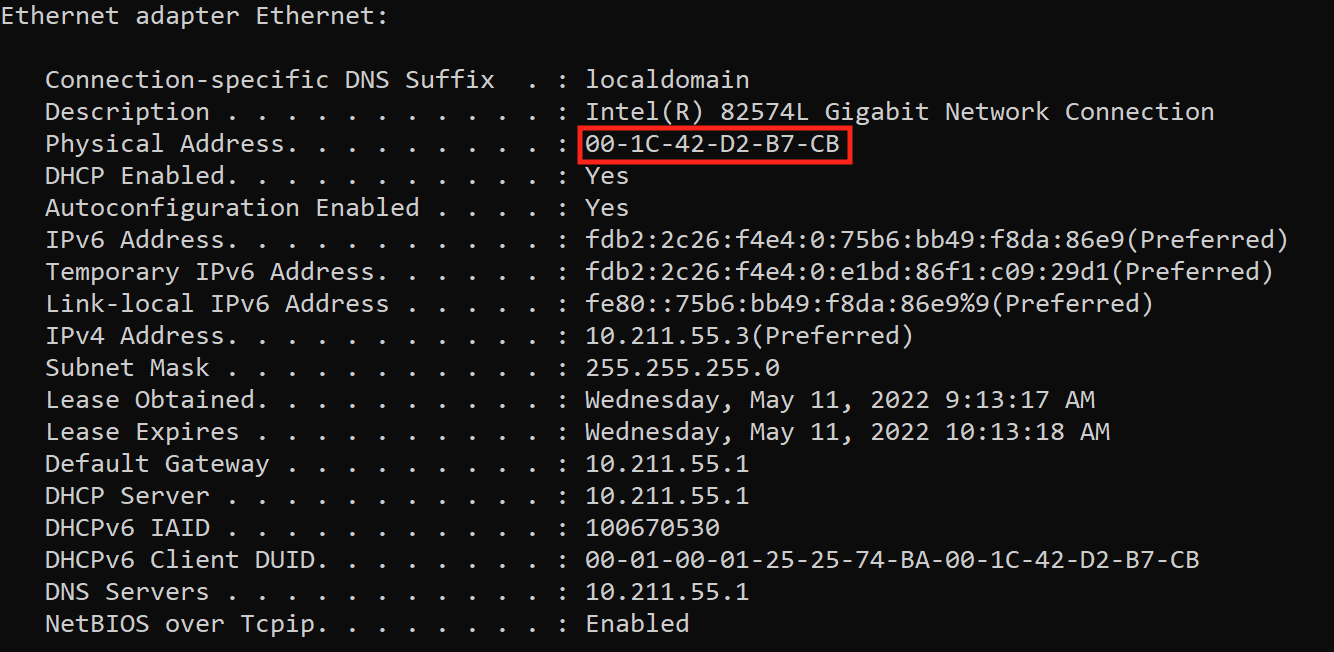
Enter your Host NIC address (without dashes) and click the required checkbox. You do not need to select any of the optional Radiant Free IP. Then click the “Generate License” button.
After receiving the license file (license.dat), follow the instructions in the email about how to install the license. You must:
- Copy the
license.datfile to the location specified in the email (<sw_install>\license\license.daton Windows).<sw_install>is probablyC:\lscc\radiant\2024.1or similar if you installed it in the default location). When you open Radiant for the first time, you’ll probably be prompted to select this license location in the FlexNet License Finder window. - Create a new
LATTICE_LICENSE_FILEsystem environment variable pointing to the path of your license file<sw_install>\license\license.dat(instructions). - Create a new
LM_LICENSE_FILEsystem environment variable pointing to the path of your license file.
Although the step to create the LM_LICENSE_FILE isn’t listed in the installation instructions in the email, it seems to be required to successfully license QuestaSim. The instructions to create this variable are listed in the Licensing User Guide for Windows.
This should ensure that both Radiant and QuestaSim are properly licensed and the files are correctly linked.
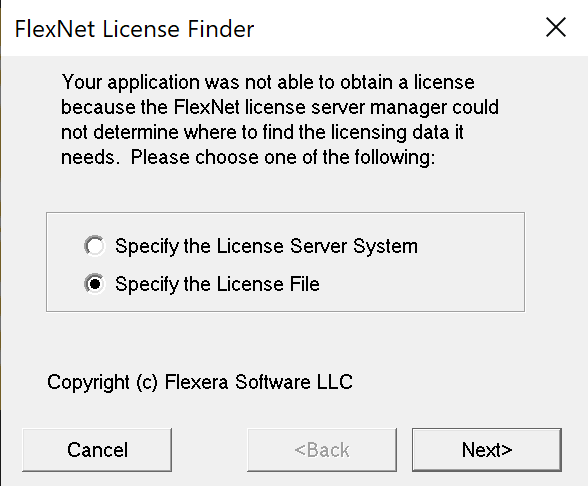
You can also check the license paths afterwards by using the License Debug Tool under the Help menu.